Selected Answers to Problem Set 6
1. Rewriting the equation y = a + bx in matrix form, we get:
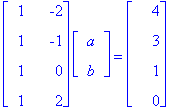
To solve for X, we need to multiply both sides by the adjoint of A. We already proved in class that the adjoint of A is the transpose of A (A* = AT). Therefore, ATAX = ATY.
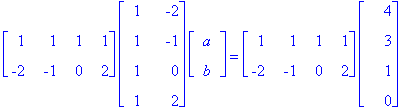
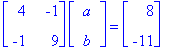
We have 9a - b = -11 and -a + 4b = 8. This is a simple linear equation that equates to a = -36/35 and b = 61/35.
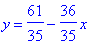
2. The same method applies as in problem one. We rewrite the equation y = c + a*sin(Pi*t/6) + b*cos(Pi*t/6) as a matrix equation: AX = Y.
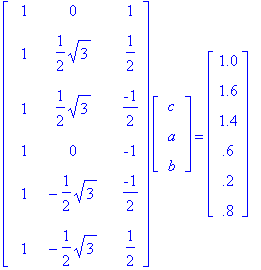
To solve for X, we need to multiply both sides by AT. Therefore, ATAX = ATY.
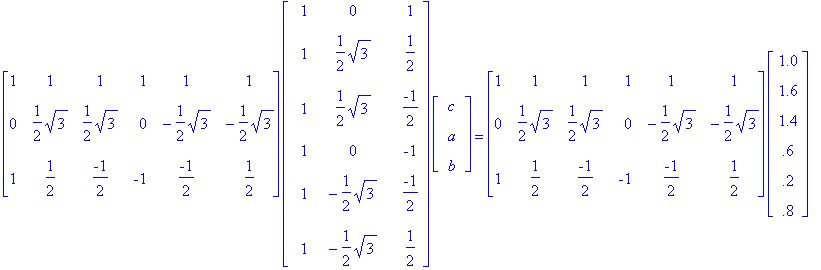
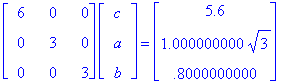
We have 3a = sqrt(3), 3b = 0.8, and 6c = 5.6. Therefore a = sqrt(3) / 3, b = 4/15, and c = 14/15.
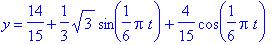
3. First rewrite the original equation to fit a linear system.
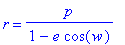
On one side of the equation we want p multipled by something and e multiplied by something. Rewriting to fit this idea gives us this:
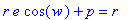
We can solve just as above then.
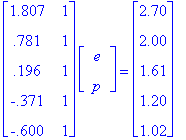
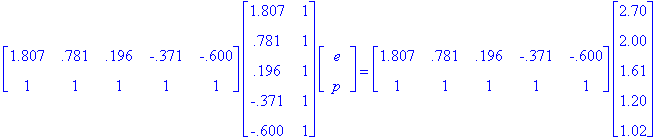
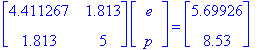
Therefore, we get p = 1.454 and e = 0.694.
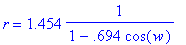
4.
a) 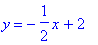
|
b) 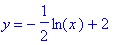
|
c) 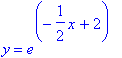
|
d) 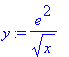
|
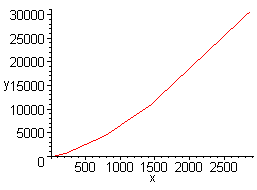
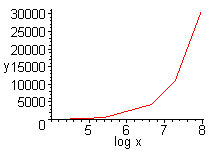
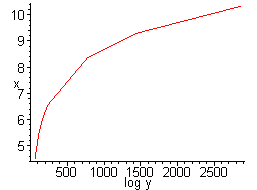
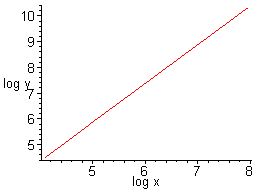
5. Here are the four equations plotting x, y, log x, and log y together. Notice that the last one, plotting log x versus log y, is the most linear.
|
|
|
|
From the linear squares equations we get that in y = ax + b, a = 1.5063 and b = -1.6591. This equates to log(T) = 1.5063 log(r) - 1.6591. Solving for T, we get T = 0.02 r^(1.5063). Recall that these measurements are not exact; we therefore can assume that the exponent on r is 3/2, which equates to T^2 = r^3, Kepler's Law.
6. Function (a) does not manipulate the object; it simply translates it. The object moves horizontally by four and vertically by two.
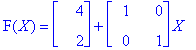
Function (b) translates horizontally by four and vertically by negative two, but it also stretches e2 by a factor of two.
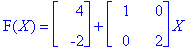
Function (c) flips the object across the e2-axis, stretches it vertically by a factor of two, then translates it. The translation is done after the manipulation; had it been done before the translation would have been forward one and up one because the flip would negate the horizontal translation.
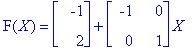
Function (d) skews the object so that it's new x-coordinate is the old x-coordinate plus the y-coordinate. The function also translates the new skewed object +1 in both directions.
7. Put answer here.